Answer:
 is the equilibrium constant,
is the equilibrium constant,
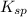 , of the generic salt
, of the generic salt
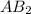 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Solubility product constant : It is defined as the product of the concentration of the ions present in a solution raised to the power by its stoichiometric coefficient in a solution of a salt. This takes place at equilibrium only. The solubility product constant is represented as,
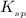 .
.
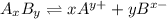
![K_(sp)=[A^(y+)]^x* [B^(x-)]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/egkcjmn027ut788hi6f22zllemn6f7ze4r.png)
Equilibrium concentration for a generic cation =
![[A^(2+)]=0.00253 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ckcozim2er4nc4pau9muispvgw9q9vt9xs.png)
Equilibrium concentration for a generic anion =
![[B^(-)]=0.00506 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5dbz8pnz0bey0r11t1s1td0ed0ddmxvlhh.png)
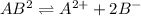
The expression of solubility product is given as:
![K_(sp)=[A^(2+)][[B^-]]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/mu9l6u3tuo60s7lhgbdon866itzqu4sgrk.png)
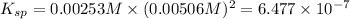
 is the equilibrium constant,
is the equilibrium constant,
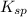 , of the generic salt
, of the generic salt
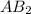 .
.