Step-by-step explanation:
Relation between work, pressure and volume is as follows.
W =
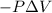
where, W = work = -927 J (as energy is released so, work is done by the system)
P = pressure = 656 torr
=
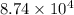 Pa (as 1 torr = 133.3 Pa)
Pa (as 1 torr = 133.3 Pa)
Initial volume
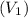 = 42
= 42
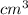
=
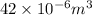 (as 1 m = 100 cm)
(as 1 m = 100 cm)
Hence, calculate the final volume as follows.
W =
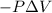
-927 J =
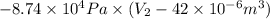
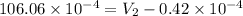
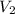 =
=
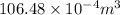
= 10.6 L (as 1
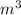 = 1000 L)
= 1000 L)
= 11 L (approx)
Thus, we can conclude that the gases expand 11 L against a constant pressure of 656 torr.