Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that the specific heat capacity of Liver
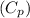 is 3.59 kJ
is 3.59 kJ
It is given that :
Initial temperature of Liver = Body temperature =
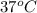 = 310 K
= 310 K
Final temperature of Liver = 180 K
Relation between heat energy, mass, and change in temperature is as follows.
Q =
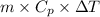
Now, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
Q =
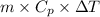
Q =
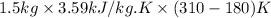
= 700.05 kJ
Therefore, we can conclude that amount of heat which must be removed from the liver is 700.05 kJ.