Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction equation will be as follows.
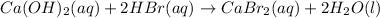
So, according to this equation, 1 mole
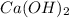 = 2 mol HBr = 1 mol
= 2 mol HBr = 1 mol
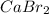
Therefore, calculate the number of moles of calcium hydroxide as follows.
No. of moles of
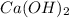 =
=
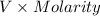
=
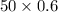
= 30 mmol
Similarly, calculate the number of moles of HBr as follows.
No. of moles of HBr =
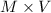
=
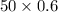
= 30 mmol
This means that the limiting reactant is HBr.
So, no. of moles of
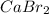 =
=
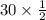
= 15 mmol
Hence, calculate the amount of heat released as follows.
Heat released in the reaction(q) =
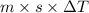
as, m = mass of solution
and, Density =
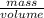
or, mass = Density × Volume
= 1.08 g/ml \times (50 + 50) ml
= 108 g
where, s = specific heat of solution = 4.18 j/g.k
and, change in temperature
 =
=
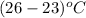
=
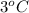
Hence, the heat released will be as follows.
q =
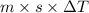
q =
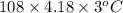
= 1354.32 joule
or, = 1.354 kJ (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Also,
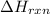 =
=
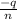
=
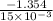
= -90.267 kJ/mol
Thus, we can conclude that the enthalpy change for the given reaction is -90.267 kJ/mol.