Answer:
[HI]i = 0.20 M
[HI]e = 0.07 M
Step-by-step explanation:
For a generic equation aA + bB ⇄ cC + dD, the constant of equilibrium (Kc) is:
![Kc = ([C]^cx[D]^d)/([A]^ax[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/aluwjelaqkxmyak3lxpjv5eji10y6280r7.png)
So, let's determinate the molar concentrations in the equilibrium for the reaction given. Let's call the initial concentration of HI Z:
H₂(g) + I₂g) ⇄ 2HI(g)
0.11 0.11 Z Initial
-x -x +2x Reacts (stoichimetry is 1:1:2)
0.11-x 0.11-x Z+2x Equilibrium
The equilibrium concentrations of H₂ and I₂ are 0.045 M, so:
0.11 - x = 0.045
-x = 0.045 - 0.11
-x = -0.065
x = 0.065
The equilibrium concentration of HI is [HI]e = Z + 0.13
So:
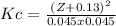
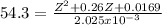
Z² + 0.26Z + 0.0169 = 0.10996
Z² + 0.26Z - 0.0930 = 0
For Baskhara:
Δ = (0.26)² - 4x1x(-0.0930)
Δ = 0.4396
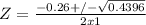
Z must be positive, so:
Z = (-0.26 + 0.6630)/2
Z = 0.20 M
[HI]i = 0.20 M
[HI]e = 0.20 - 0.13 = 0.07 M