Answer:
a) Q = 6.1875x10⁻³
b) The direction of the reaction is to form the products.
c) [Cl₂]e = 0.094 M
[NO]e = 0.190 M
[NOCl]e = 0.140 M
Step-by-step explanation:
a) Q is the reaction quotient, and for a generic reaction aA + bB ⇄ cC + dD it is
![Q = ([C]^cx[D]^d)/([A]^ax[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bge825y2bbvenl0aia0vesirzij1dqkvp8.png)
Which is the same equation for Kc, but in Kc expressions, the concentrations are in the equilibrium. Q is calculated at any time. So, for the reaction given
2NOCl(g) ⇄ 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
![Q = ([Cl2]x[[NO]^2)/([NOCl]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t7cp77du68ntm2vy8a1xnbtdvi6blcp8su.png)
[Cl₂] = 0.220/5.00 = 0.044 M
[NO] = 0.450/5.00 = 0.090 M
[NOCl] = 1.20/5.00 = 0.240 M
Q = (0.044)x(0.090)²/(0.240)²
Q = 6.1875x10⁻³
b) Q < Kc, which means that there are fewer products to what are needed to the equilibrium. So the direction of the reaction is to form the products.
c)
2NOCl(g) ⇄ 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
0.240 0.090 0.044 Initial
-2x +2x +x Reacts (stoichiometry is 2:2:1)
0.240-2x 0.090+2x 0.044+x Equilibrium
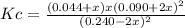
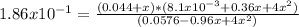
3.564x10⁻⁴+0.01584x+0.176x²+8.1x10⁻³x+0.36x²+4x³ = 0.010714-0.17856x+0.744x²
4x³ - 0.208x² + 0.2025x - 0.01036 = 0
Solving this third grade equation in a computer program:
x = 0.05 M
So:
[Cl₂]e = 0.044 + 0.05 = 0.094 M
[NO]e = 0.090 + 2x0.05 = 0.190 M
[NOCl]e = 0.240 - 2x0.05 = 0.140 M