Answer:
Longest wavelength = 343.7 nm
Solution and Explanation:
In this question we need to first use the concept of energy of a photon.
Energy of a photon, E, is given by the formula, E = hf, where h is the plank's constant, f is the frequency.
But since, f is given by dividing speed, c, by wavelength, λ, then;
E = hc/λ
We are given 348 kJ/mol required to break carbon-carbon bonds.
We know that; 1 mole of bonds = 6.022 × 10^23 bonds.
We are required to find the longest wavelength with enough energy to break the C-C bonds.
This can be worked out in simple steps:
Step 1: Energy required to break one bond (kJ/bond)
1 mole of bonds = 6.022 × 10^23 bonds.
Therefore;
348 kJ = 6.022 × 10^23 bonds.
Thus;
1 bond = 348 kJ ÷ 6.022 × 10^23 bonds.
= 5.778 x 10^-22 kJ
But; 1000 joules = 1 kJ
Hence; energy per bond = 5.778 x 10^-19 Joules
Step 2: Energy per photon
Breaking one bond requires energy equivalent to energy of a photon.
Therefore;
1 photon = 5.778 x 10^-19 Joules
= 5.778 x 10^-19 J/photon
Step 3: Calculating the wavelength
From the equation of energy of a photon;
E = hc/λ
h is the plank's constant = 6.626 × 10^-34 J/s
c is the speed of light in vacuum = 2.9998 × 10^8 m/s
E is the energy of a photon = 5.778 x 10^-19 Joules
Therefore, making λ (wavelength) the subject;
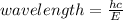
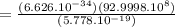
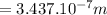
= 3.437 x 10^-7 m
But; 1 nm = 10^-9 m
Thus;
wavelength = 343.7 nm
Therefore, the longest wavelength of the radiation will be 343.7 nm