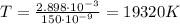Answer:
19320 K
Step-by-step explanation:
The temperature of a star is related to its peak wavelength by Wien's displacement law:
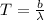
where
T is the absolute temperature at the star's surface
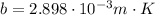 is Wien's displacement constant
is Wien's displacement constant
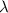 is the peak wavelength
is the peak wavelength
Here we have
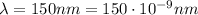
Substituting into the equation, we find