Answer:
The mouse consumed 0,04064 g of oxygen.
Step-by-step explanation:
To answer this question you can use gas law (PV=nRT) solving for moles of air that are proportional to moles of oxygen. These moles most be converted to grams with molecular weight:
n = PV/RT
Where, at initial conditions:
P is pressure (761,0torr×
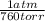 ) = 1,0013 atm
) = 1,0013 atm
V is volume 2,40 L
R is gas constant 0,082 atmL/molK
T is temperature 306 K
Solving, moles of aire are: 0,09577 moles
21% of air is oxygen, thus:
0,09577×0,21 = 0,02011 initial moles of oxygen
The final moles of oxygen are:
n = PV/RT
With the same initial conditions just changing pressure:
P is 712,9torr×
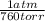 = 0,9380 atm
= 0,9380 atm
Final moles are: 0,08972 moles of air
The moles of oxygen are:
0,08972×0,21 = 0,01884 final moles of oxygen
Thus, moles of oxygen consumed by the mouse are:
0,02011 - 0,01884 = 1,27x10⁻³ moles
In grams:
1,27x10⁻³ moles ×
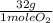 = 0,04064 g of O₂
= 0,04064 g of O₂