Answer:
1. There is less variation in temperature of Aquatic habitats
2. The movement of water up trees results from capillary action.
3. Provides insulation to aquatic habitats
4. Evaporative cooling
Step-by-step explanation:
1. The specific heat of water is high and is characterized as measure of heat required to result in the rise in temperature of 1 g of a substance by
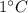 .
.
Due to this, water can limit changes in temperature thus there isn't much variation in temperature.
2. Capillary action is the motion of water inside the spaces of a permeable material because of forces of cohesion, adhesion and surface tension.
Thus Cohesion forces results in the motion of water up trees.
3. Water has one most significant property where solid structure is less dense than fluid or liquid form that protects aquatic environments. As water in its solid form is less dense, in this manner ice coasts on the lake's surface that protects the water beneath from solidifying and valuable to aquatic life forms.
4. Heat of vaporization of water is high, which is characterized as the measure of energy expected to transform 1 gram of a liquid substance to a gas at steady temperature.
Along these lines when water particles evaporates, the surface they dissipate from gets cooler, referred to as evaporative cooling.