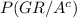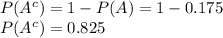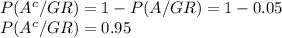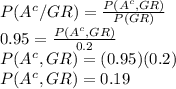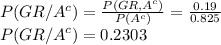Answer:
a. 17.5 %
b. 0.2303
Explanation:
Let's start defining the conditional probability :
Suppose two events A and B where
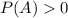 and
and
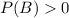
and P(A ∩ B) = P(A,B) where (A ∩ B) is the event where A and B occur both at the same time.
The conditional probability :
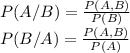
Let's define the following events :
A : ''Randomly chosen person had accident in a fixed year''
GR : ''The person belongs to good risks classification''
AR : ''The person belongs to average risks classification''
BR : ''The person belongs to bad risks classification''
The information given is :
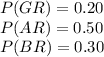
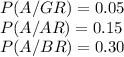
a.
We need to calculate
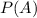
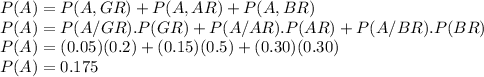
Then 17.5% of people have accidents in a fixed year
b. If U is an event ⇒
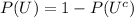
Where
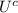 is the event where U does not occur
is the event where U does not occur
We need to calculate :