Answer:
Time=185.459 s in seconds
Time=3.091 min in minutes
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
density=2700 kg/
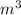
Diameter=44 μm
radius=diameter/2
radius=44/2=22 μm
Volume=(4/3)*π*
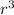
Volume=
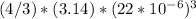
Volume=
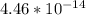
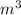
mass=Volume*density
mass=2700*4.46*
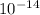
mass=1.2042*
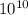
density of air=1.1839 kg/
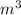
Projected area=
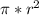
Projected area=
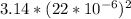
Projected area=1.5197*
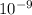
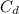 for sphere=0.47
for sphere=0.47
Terminal velocity=v=
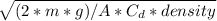
where density is the air density.
Substitute values we will get
v=1.6715 m/s
Time=distance/velocity
height=distance=310 m
Time=310/1.6715
Time=185.459 s in seconds
Time=3.091 min in minutes