Answer:
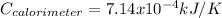
ΔcH
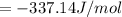
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, naphthalene has a Cp=156.1J/(mol*K) and the following equation must be applied to find the enthalpy of combustion (negative since it is about an outgoing form of energy) considering the given assumption (∆H ≈∆U)
ΔcH=Cp*ΔT
ΔcH

For the calorimeter constant, we develop:

Best regards.