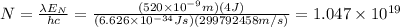Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy of a photon is given by the equation
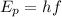 , where h is the Planck constant and f the frequency of the photon. Thus, N photons of frequency f will give an energy of
, where h is the Planck constant and f the frequency of the photon. Thus, N photons of frequency f will give an energy of
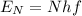 .
.
We also know that frequency and wavelength are related by
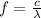 , so we have
, so we have
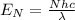 , where c is the speed of light.
, where c is the speed of light.
We will want the number of photons, so we can write
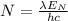
We need to know then how much energy do we have to calculate N. The equation of power is
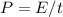 , so for the power we have and considering 1 second we can calculate the total energy, and then only consider the 4% of it which will produce light, or better said, the N photons, which means it will be
, so for the power we have and considering 1 second we can calculate the total energy, and then only consider the 4% of it which will produce light, or better said, the N photons, which means it will be
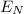 .
.
Putting this paragraph in equations:
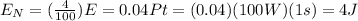 .
.
And then we can substitute everything in our equation for number of photons, in S.I. and getting the values of constants from tables: