Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Mass of the hockey puck, m = 112 g = 0.112 kg
The hockey puck is stopped at a distance of 16.8 m.
(a) Initial speed of the puck, u = 8.1 m/s
We need to find the magnitude of the frictional force. Firstly, calculating the acceleration of the puck using third equation of kinematics as :
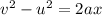
v = 0 (as it stops)
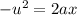
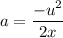
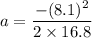
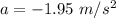
The frictional force is given by :
f = m a
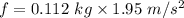
f = 0.218 N
(b) Also the frictional force is given by :
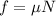
And N = mg (normal force)
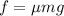
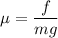
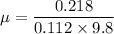
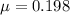
Hence, this is the required solution.