Answer:
The required flow rate of air in mol/h is 20144 and the percent by mass of oxygen in the product gas is 23,1%.
Step-by-step explanation:
The air of 9 mole% methane have an average molecular weight of:
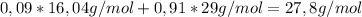
And a flow of 700'000g/h÷27,8g/mol = 25180 mol/h
In the reactor where methane solution and air are mixed:
In = Out
Air balance:
91% air×25180 mol/h + 100% air×X = 95%air×(X+25180)
Where X is the flow rate of air in mol/h.
Solving, X = 20144 mol air/h
The air in the product gas is:
95%×(20144 + 25180) mol/h = 43058 mol air× 21%O₂ = 9042 mol O₂ ×32g/mol = 289 kg O₂
43058 mol air×29g/mol 1249 kg air
Percent mass of oxygen in the product gas is: =0,231 kg O₂/ kg air* 100 = 23,1%
I hope it helps!