Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Voltage to accelerate electrons to hit a copper plate and produce X-rays,
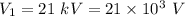
Using the conservation of energy for the electrons as :
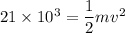
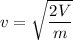
m is the mass of electron
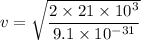
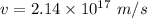
For the proton, mass,
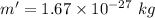
Now using the conservation of energy for the protons. We get :
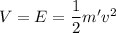
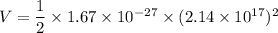
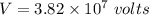
Hence, this is the required solution.