Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Densities of both the reactant solutions = 1.07 g/mL.
Specific heat = 4.18
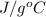
Volume of HCl = 32.8 ml
Volume of NaOH = 66.3 ml
The reaction will be as follows.

Since, density is mass divided by volume. Hence, calculate the mass of HCl as follows.
Mass of HCl = Density × Volume of HCl
=
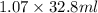
= 35.096 g
Similarly, mass of NaOH will be calculated as follows.
Mass of NaOH = Density × Volume of NaOH
=
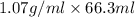
= 70.941 g
Therefore, total mass will be as follows.
Total mass = Mass of HCl + Mass of NaOH
= 35.096 g + 70.941 g
= 106.037 g
Change in temperature will be calculated as follows.
 =
=
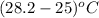
=
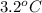
Therefore, calculate the heat of reaction as follows.
q =
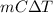
=
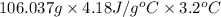
= 1418.35 J
or, = 1.418 kJ (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
No. of moles of HCl = Molarity × Volume
= 0.5 M × 32.8 ml
= 16.4 mol
No. of moles of NaOH = Molarity × Volume
= 0.5 M × 66.3 ml
= 33.15 mol
So, HCl is the limiting reagent and heat of reaction produces by per mole of NaCl will be calculated as follows.
Heat released for 1 mole of NaCl =
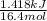
= 0.0864 kJ/mol
Thus, we can conclude that the heat of reaction per mole of NaCl is 0.0864 kJ/mol.