Answer:
The impulse will be equal
Step-by-step explanation:
Impulse is defined as the change in momentum.
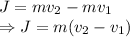
Where,
m = Mass of the brick
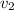 = Final velocity of the brick = 0
= Final velocity of the brick = 0
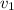 = Initial velocity of the brick = 2.5 m/s
= Initial velocity of the brick = 2.5 m/s
So,
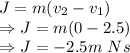
As, it can be seen here the time taken is irrelevant when it comes to calculating impulse. In both cases of brick and gelatin the initial and final velocities are same hence, the impulse will be equal.