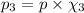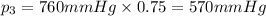Answer:
76 mmHg is the partial pressure of oxygen on this new planet.
Step-by-step explanation:
Atmospheric pressure on air on earth = 760 mmHg
On an unknown planet :
Oxygen makes up 10% of the atmosphere.
The mole fraction of oxygen gas can be written as =
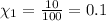
Carbon dioxide makes up 15% of the atmosphere.
The mole fraction of carbon dioxide gas can be written as =
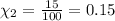
Nitrogen makes up the remaining 75% of the atmosphere.
The mole fraction of nitrogen gas can be written as =
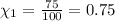
Atmospheric pressure of air on unknown planet,p= 760 mmHg (given)
Partial pressure of gases can be calculated by the help o Dalton's law of partial pressure:
Partial pressure of oxygen gas :
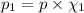
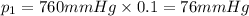
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide gas :
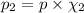
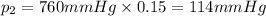
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas :