Answer:
a= 17.877 m/s² : Magnitude of the acceleration of the flea
β = 88.21° : Direction of the acceleration of the flea
Step-by-step explanation:
Conceptual analysis
We apply Newton's second law:
∑F = m*a (Formula 1)
∑F : algebraic sum of the forces in Newton (N)
m : mass in kilograms (kg)
a : acceleration in meters over second square (m/s²)
Problem development
Look at the flea free body diagram in the attached graphic
The acceleration is presented in the direction of the resultant force (R) applied over the flea .
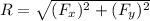
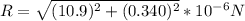
R= 10.905*10⁻⁶ N
We apply the formula (1) to calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the flea
∑F = m*a m = 6.1 * 10⁻⁷ kg
R = m*a
a= R/m
a= (10.905*10⁻⁶) / (6.1 * 10⁻⁷ )
a= 17.877 m/s²
β: Direction and magnitude of the acceleration of the flea
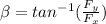
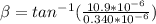
β = 88.21°