Answer:
the mole fraction of hexane in your sample is 0.04
Step-by-step explanation:
This is solved by a system of equations, that is, a system that in this case has 2 linear equations with two unknown variables.
First you define your variables:
- xh: mole fraction of hexane
- xt: mole fraction of toluene
The molar fraction is the relationship between the moles of hexane and toluene in the solution, and its sum must be equal to 1. This is represented by the equation: xh+xy=1 Equation (A)
On the other hand you know that pure hexane has a refractive index of 1.375, pure toluene has a refactive index of 1.497 and a distillate sample has a refractive index of 1.391.
That the simple distillate has that index means that the sum of the fraction of hexane present and the toluene present generates that value. Knowing the refractive indices of pure compounds, the equation can be called:
1.375*xh+1.497*xy=1.391 Equation (B)
Now you have armed the system of equations to solve:
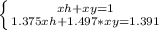
One of the most used ways to solve a system of equations is by substitution, which consists in isolating one of the variables of one of the equations and replacing it in the other.
Isolating xy from the first equation and replacing the value in the second equation gives:
1.375*xh+1.497*(1-xh)=161
Isolating the value of xh, you get: xh=0.04
By replacing the value of xh in any equation, you get xy: xy=0.96
This means that the mole fraction of hexane in your sample is 0.04 and the mole fraction of toluene in your sample is 0.96