Answer: The mass of methanol in the sample is 0.1002 grams
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
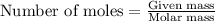 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of carbon dioxide = 0.367 g
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44.0 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
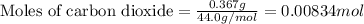
Let the mass of methanol in the sample be 'x' grams.
We are given:
Mass of the mixture of methanol and ethanol = 0.220 g
Mass of methanol = x g
Mass of ethanol = (0.220 - x) g
Given mass of methanol = x g
Molar mass of methanol = 32 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
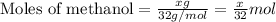
Given mass of ethanol = (0.220 - x) g
Molar mass of ethanol = 46 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
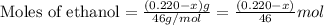
- The chemical equation for the combustion of methanol follows:
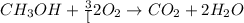
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of methanol produces 1 mole of carbon dioxide
So,
/(1)* (x)/(32)=(x)/(32)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hco26wlduskrqn1ulu33rvfqi7z159u4bu.png) moles of carbon dioxide
moles of carbon dioxide
- The chemical equation for the combustion of ethanol follows:

By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of ethanol produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide
So,
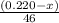 moles of ethanol will produce =
moles of ethanol will produce =
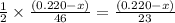 moles of carbon dioxide
moles of carbon dioxide
Total moles of carbon dioxide:
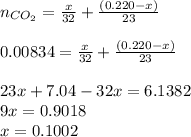
Hence, the mass of methanol in the sample is 0.1002 grams