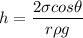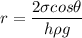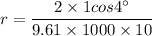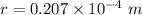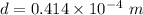Answer:
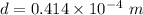
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that
P = 4 KPa
Contact angle = 6°
Surface tension = 1 N/m
Lets assume that atmospheric pressure = 100 KPa
Lets take that density of water =
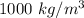
So the capillarity rise h
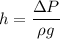
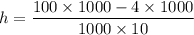
h= 9.61 m
We know that for capillarity rise h