Answer:
The time for the surface temperature to reach 25 ◦C is 3.24 hr
Step-by-step explanation:
Assumptions
1. 1-D heat conduction
2. constant thermal properties
3. the heat transfer coefficient is constant & uniform over the surface.
Properties
k = 0.79 W/m · ◦C
α = 5.94 × 10−7 m^2/s
ρ = 1600 kg/m^3
Cp = 0.84 kJ/kg · ◦C
Step 1: Check the Biot number
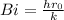
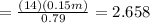
As Bi > 0.1 hence lumped system analysis will not considered.
Check the Fourier number.
From Table 18-1
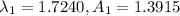
From Table 18-2, we can find
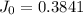
The Fourier number is determined as
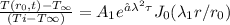
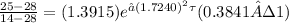
solving τ
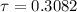
Since τ > 0.2, the one term approximation or the Heisler charts can be used.
The time for the surface temperature to reach 25 ◦C is
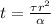
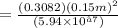
= 11674.24 s = 3.24 hours