Answer : The heat of sublimation of Li(s) is 179.5 kJ/mole
Explanation :
The formation of lithium iodide is,
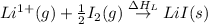
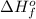 = enthalpy of formation of lithium iodide
= enthalpy of formation of lithium iodide
The steps involved in the born-Haber cycle for the formation of
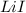 :
:
(1) Conversion of solid lithium into gaseous lithium atoms.
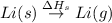
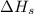 = sublimation energy of lithium
= sublimation energy of lithium
(2) Conversion of gaseous lithium atoms into gaseous lithium ions.
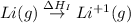
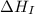 = ionization energy of lithium
= ionization energy of lithium
(3) Conversion of molecular gaseous iodine into gaseous iodine atoms.
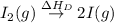
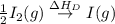
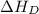 = dissociation energy of iodine
= dissociation energy of iodine
(4) Conversion of gaseous iodine atoms into gaseous iodine ions.
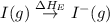
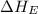 = electron affinity energy of iodine
= electron affinity energy of iodine
(5) Conversion of gaseous cations and gaseous anion into solid lithium iodide.
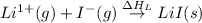
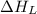 = lattice energy of lithium iodide
= lattice energy of lithium iodide
To calculate the overall energy from the born-Haber cycle, the equation used will be:
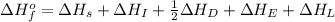
Now put all the given values in this equation, we get:
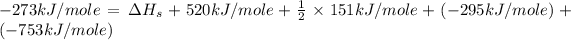
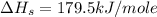
Therefore, the heat of sublimation of Li(s) is 179.5 kJ/mole