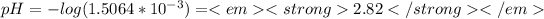Answer:
pH=2.82
Step-by-step explanation:
pH is a scale used to indicate if a water-based solution is acidic or basic, and is defined by the following equation:
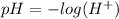 Equation (1)
Equation (1)
In aqueous solutions there are no ions
 , because the proton is transferred to
, because the proton is transferred to
 to form hydronium ions,
to form hydronium ions,
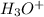 . Thus, we can determine the pH of the solution, finding the molar concentration of
. Thus, we can determine the pH of the solution, finding the molar concentration of
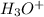 ions:
ions:
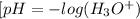 Equation (2)
Equation (2)
The solution prepared contains two weak acids, each one undergoes an equilibrium process with the corresponding equilibrium constant Ka, as it is represented in the following reaction for a weak acid HA:
HA +
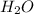 ⇔
⇔
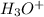 +
+
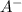
The equilibrium constant is defined by the equilibrium concentration of products over reactants:
![k= ([H_3O^(+)][A^(-)])/([HA][H_2O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/vp26j58e9xemqgvzs0g0l0yd17v8rp0s8a.png) Equation (3)
Equation (3)
However, the molar concentration of water is essentially constant for reactions in aqueous solutions, then the acid dissociation constant is defined as follow:
![k_a=K[H_2O]= ([H_3O^(+)][A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/j1z4xjzen97m1ngv6beo6ofye5gptc6594.png) Equation (4)
Equation (4)
Information for
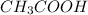 :
:
Reaction:
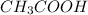 +
+
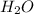 ⇔
⇔
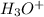 +
+
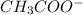
Initial moles per Liter: 0.125 M + A ⇔ 0 + 0
Reacting moles per liter: -x + -x ⇔ x + x
Equilibrium mole per liter: 0.125 M-x + A-x ⇔ x + x
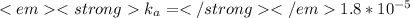
Information for
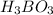 :
:
Reaction:
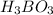 +
+
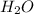 ⇔
⇔
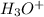 +
+
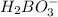
Initial moles per Liter: 0.125 M + A ⇔ 0 + 0
Reacting moles per liter: -y + -y ⇔ y + y
Equilibrium mole per liter: 0.125 M-y + A-y ⇔ y + y
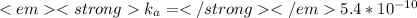
Replacing the equilibrium information of each acid in equation 4, we get:
For
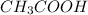 :
:
![1.8*10^(-5) =([x][x])/([0.125-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/l9q7v0bgzmjxkjyys79ququd1v7hxv8l8r.png) Equation (5)
Equation (5)
For
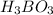 :
:
![5.4*10^(-10) =([y][y])/([0.125-y])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/5r1sq2liqvxs2raaki8qceeply2yfahtu3.png) Equation (6)
Equation (6)
Solving equation 5 and 6:
For
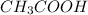 :
:
![x = [H_(3)O^(+)] = 1.49*10^(-3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ntgq1er9g80i900bzmquc87whnq1wbldck.png)
For
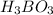 :
:
![y = [H_(3)O^(+)] = 1.64*10^(-6)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/y0zsmbj37fzpl8f470xz0au9i1b3jae15j.png)
Due to both acids are in the same solution, the total concentration of
![[H_(3)O^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9q4wjqeu25nf3f930xkrlsn4yiv6nzirb8.png) is (x+y)
is (x+y)
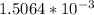 . Replacing this concentration in equation 2, we get:
. Replacing this concentration in equation 2, we get: