Answer:
-15.24 kJ/mole of LiOH
Step-by-step explanation:
General considerations:
-A coffee-cup calorimeter is a device that works at constant pressure. Since enthalpy (ΔH) is defined as a heat flow at constant pressure, the coffee-cup calorimeter is usually used to measure enthalpy changes in processes at constant pressure.
-The high heat capacity of calorimeter indicates its difficulty to vary its temperature.
-The calorimeter absorbs a negligible amount of heat.
Information given in the statement:
Intial temperature = 23°C
Final temerature = 34.65°C
Mass of LiOH= 10 g LiOH
Mass of solution =
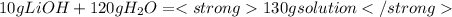
Specific heat capacity of the solution =
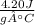
Converting specific heat capacity to kJ/(g°C) =
/(g°C)=(4.20 J)/(g°C)*(1 kJ)/(1000 J)=\<strong>frac{0.00420 kJ}{g°C}</strong>](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/au4ir4ck34magz0e6e4wwbc3jeb06qt41z.png) [/tex]
[/tex]
Calculations:
To determine the dissolution enthalpy of LiOH, we can use the following equations:
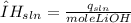 Equation 1
Equation 1
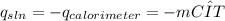 Equation 2
Equation 2
![mole of LiOH=(mas of LiOH)/(Molecular weight of LiOH) <em><strong>Equation 3</strong></em></p><p> </p><p>Where:</p><p>[tex]ΔH_(sln)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/n34e64uc2jxogxyfqlasin5a56ta1qlfox.png) = enthalpy of dissolution per mole of LiOH (kJ/mole).
= enthalpy of dissolution per mole of LiOH (kJ/mole).
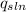 = heat released by dissolution (kJ).
= heat released by dissolution (kJ).
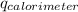 =heat absorbed by the solution in calorimeter (kJ) .
=heat absorbed by the solution in calorimeter (kJ) .
m=mass of solution (g).
C=specific heat capacity of the solution (kJ/g°C).
ΔT=chage of temperature of the solution in calorimeter, final temperature minus initial temperatrue (°C).
Molecular weight of LiOH=23.95 g/mole
Replacing the given data in equations 1, 2 and 3, we get:
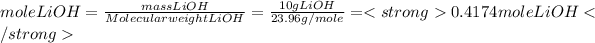
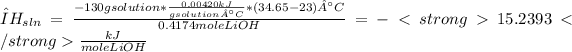
Note: Usually exothermic reactions like LiOH dissolutions, that release heat, results in negative enthalpy.