(a) 278.4 m
First of all, we need to find the time it takes for the package to reach the ground. We can use the equation for the vertical motion:
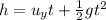
where
h = -165 m is the vertical displacement
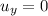 is the initial vertical velocity
is the initial vertical velocity
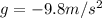 is the acceleration of gravity
is the acceleration of gravity
t is the time
Substituting and solving for t,
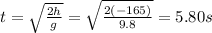
During this time interval, the package travels with a horizontal speed of
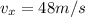 (the initial velocity of the plane)
(the initial velocity of the plane)
So, the horizontal distance covered is
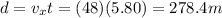
So, the package landed 278.4 m far from the point directly below the releasing point.
(b) 48 m/s
Along the horizontal direction, there is no force (if we neglect air resistance), therefore no acceleration, according to Newton's second law:
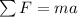
so a = 0 since
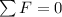 .
.
This means that the horizontal component of the velocity remains constant; since its initial value is
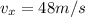
Then it will remain constant for the whole motion, and therefore it will still be 48 m/s when the package reaches the ground.