Answer:
The turnover number is the maximum substrate quantitiy converted to product per enzyme and per second. It can be calculate as follows:
![k_c = (V_(max))/([E])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/gh8zztq7x9md5w7neknppawigroezqoj02.png) with
with
![[E]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/w29mkjwfdyltwlzblv8c7hun4kihr9rixn.png) active enzyme concentration.
active enzyme concentration.
In this case we have Vmax an data to calculate
![[E]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/w29mkjwfdyltwlzblv8c7hun4kihr9rixn.png)
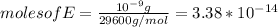
![[E]=(3.38*10^(-14))/(0.01 L)=3.38*10^(-12) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/mcaz6gl096bw502ac631epzfofcrp11vq7.png)
Now
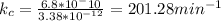
it is not like any option.
If we assume that
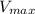 have the non usual units of
have the non usual units of
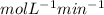 and it is
and it is
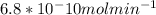
So we need divide by the moles of E (in place of [E])
Now
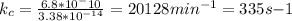
(pass from
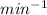 to
to
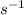 dividing by 60)
dividing by 60)