Answer:
Molar flow rate is 10.068 mole/h
Mole fraction is 0.0232
Solution:
As per the question:
Amount of ammonia absorbed by water = 96% = 0.96
Initially, the weight = 5 kg
The final weight = 5.25 kg.
Therefore,
96% of the initial amount of Ammonia is represented by:
Final weight - Initial weight
5.25 – 5.00 = 0.250 kg = 250 g
250 g represents 96% of the initial ammonia.
Now,
Initially, weight of ammonia =
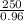 = 260.416 g
= 260.416 g
Now,
Ammonia present in the exit gas stream is given by:
260.416 - 250 = 10.416 g
Now,
Weight of methane = Weight of ethane = 260.416 g
So,
Moles of methane =
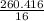 = 16.276 moles
= 16.276 moles
Moles of ethane =
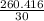 = 8.6805 moles
= 8.6805 moles
Mole of ammonia =
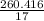 = 15.318 moles
= 15.318 moles
Total no. of moles = 16.276 + 8.6805 + 15.318 = 40.274 moles
Now,
Molar Flow Rate =
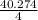 = 40.276 / 4 = 10.068 moles/h
= 40.276 / 4 = 10.068 moles/h
Therefore,
No.of moles of ammonia in the exit stream =
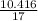 = 0.592 moles
= 0.592 moles
Therefore, in the exit stream ,
Mole fraction of ammonia =
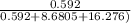
Mole fraction of ammonia = 0.0232