Answer:
For A: The reaction is lying towards right.
For B: The reaction is lying towards left.
Step-by-step explanation:
There are 3 conditions:
- When
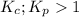 ; the reaction is product favored.
; the reaction is product favored. - When
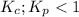 ; the reaction is reactant favored.
; the reaction is reactant favored. - When
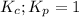 ; the reaction is in equilibrium.
; the reaction is in equilibrium.
The given chemical equation follows:
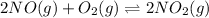
The equilibrium constant in terms of pressure given to us is
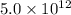
The given value is very high than 1. So, the reaction is favoring the formation of products.
Hence, the reaction is lying towards right.
The given chemical equation follows:
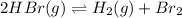
The equilibrium constant in terms of concentration given to us is
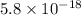
The given value is very low than 1. So, the reaction is favoring the formation of reactants.
Hence, the reaction is lying towards left.