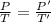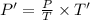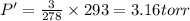Answer:
The final pressure is 3.16 torr
Solution:
As per the question:
The reduced pressure after drop in it, P' = 3 torr =
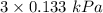
At the end of pumping, temperature of air,
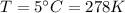
After the rise in the air temperature,
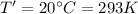
Now, we know the ideal gas eqn:
PV = mRT
So
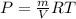
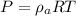 (1)
(1)
where
P = Pressure
V = Volume
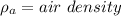
R = Rydberg's constant
T = Temperature
Using eqn (1):
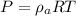
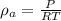
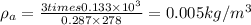
Now, at constant volume the final pressure, P' is given by: