Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The statements are logically equivalent if they have the same truth tables. So let´s use truth tables in order to determine if they are logically equivalent or not:
The picture that I attached you shows the truth table for each case. As you can see in the highlight columns:
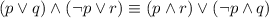
They are logically equivalent because they have exactly the same truth values between each other. Hence, we can conclude that they are logically equivalent.