Answer:
We know that force on the moving (velocity V) charge q due to magnetic field B given as
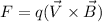
If force act for time t then energy gained by moving charge
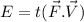
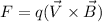
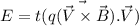
We know that
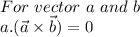
So
E=0
Now we can say that total kinetic energy of charge q will become
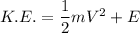
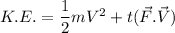
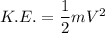
So
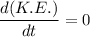 (V= constant)
(V= constant)
We can say that
K.E.= constant
So the force exerted by a magnetic field does no work on a charged particle.