From a mathematical point of view, the Schrödinger Equation is a LINEAR partial differential equation, as is a partial differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the solution and its derivatives.
For a linear differential equation, if you got two different solutions
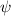 and
and
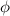 , then the linear combination
, then the linear combination
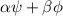 , where
, where
 and
and
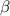 are scalars, is also a solution.
are scalars, is also a solution.
This also is valid for only one solution (think of the other solution as equal to zero,
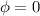 ). So, as the Schrödinger Equation is a Linear partial differential equation, then if
). So, as the Schrödinger Equation is a Linear partial differential equation, then if
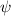 is a solution, then
is a solution, then
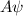 must also be a solution.
must also be a solution.
This is extremely important for physicist, as let us know that the superposition principle is valid.