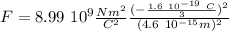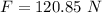Answer:
The magnitude of the electrostatic force is 120.85 N
Step-by-step explanation:
We can use Coulomb's law to find the electrostatic force between the down quarks.
In scalar form, Coulomb's law states that for charges
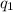 and
and
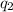 separated by a distance d, the magnitude of the electrostatic force F between them is:
separated by a distance d, the magnitude of the electrostatic force F between them is:
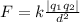
where
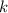 is Coulomb's constant.
is Coulomb's constant.
Taking the values:
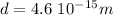
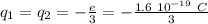
and knowing the value of the Coulomb's constant:
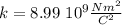
Taking all this in consideration: