Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Buffer solutions are solutions capable of maintaining their pH at approximately constant values when small amounts of acid or base are added.
A buffer solution is characterized by simultaneously containing a weak species and its conjugate pair. In other words, it has a weak acid and a salt of the same acid from a strong base or, a base and a salt of this base from a strong acid.
Two examples are:
- Mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate
- Ammonium Hydroxide and Ammonium Chloride
Given that the buffer solution is a mixture of weak acid with a salt of the same acid from a strong base, the acid will be partially dissociated according to the equation:
HA ⇔
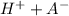
Applying the Law of Mass Action (which establishes the relationship between the masses of reagents and products in a chemical equilibrium at a given temperature) and taking into account the dissociation constant(
![Ka=([A^(-)]*[H^(+)] )/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/r1rw6wblyeskibuu00l1auog77v1eknl30.png) ) is obtained the following expression:
) is obtained the following expression:
![pH=pKa+log([A^(-) ])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bgksnep8l67a7g6gkn9zye8t9wfyryddam.png)
Where pKa represents the potential value of the acid acid constant of the weak acid,
![[A^(-) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1qxaln5h8xii99b926vw1h2iw0tr2skhmv.png) is the common anion concentration, equivalent to salt and [HA] indicates weak acid concentration which is part of the buffer solution. Consequently, the above equation can be rewritten as follows:
is the common anion concentration, equivalent to salt and [HA] indicates weak acid concentration which is part of the buffer solution. Consequently, the above equation can be rewritten as follows:
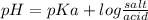
According to this equation, the pH of a solution buffer, depends on two factors:
a) The pKa value of the weak acid
b) The proportions between salt and acid concentrations
In summary, the presence of the conjugate pair causes the weak species to dissociate to a lesser extent and the presence of the weak species causes the conjugate pair to hydrolyze less.