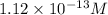Answer : The concentration of
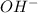 ion, pH and pOH of solution is,
ion, pH and pOH of solution is,
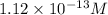 , 1.05 and 12.95 respectively.
, 1.05 and 12.95 respectively.
Explanation : Given,
Concentration of
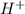 ion = 0.090 M
ion = 0.090 M
pH : It is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion or hydronium ion concentration.
The expression used for pH is:
![pH=-\log [H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ipfjz05f4cfbguiwup37xvxa7furlbuapf.png)
First we have to calculate the pH.
![pH=-\log [H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ipfjz05f4cfbguiwup37xvxa7furlbuapf.png)
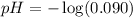
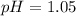
The pH of the solution is, 1.05
Now we have to calculate the pOH.
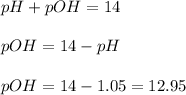
The pOH of the solution is, 12.95
Now we have to calculate the
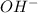 concentration.
concentration.
![pOH=-\log [OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/h1t4ubcsdqvqg0xpalkkvnwrun04y9pzd8.png)
![12.95=-\log [OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bnutnq84kwwcpkb0jgzvfpeluk0ms3bjbw.png)
![[OH^-]=1.12* 10^(-13)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xe45gq2mymg3bmilrzulcigonnb11fhzc4.png)
The
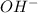 concentration is,
concentration is,