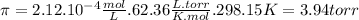Answer:
The osmotic pressure is 3.94 torr.
Step-by-step explanation:
Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of solution, which can be calculated according to the following expression:
π = M . R. T [1]
where,
π is the osmotic pressure
M is the molarity of the solution
R is the ideal gas constant (62.36 L . torr/ K . mol)
T is the absolute temperature (in Kelvin scale)
Molarity can be calculated from its definition:
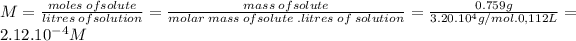
Absolute temperature can be calculated like:
K = °C + 273.15
K = 25.00 + 273.15 = 298.15 K
Replacing this data in equation 1: