Answer:
The ionization equation is
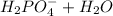 ⇄
⇄
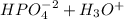 (1)
(1)
Step-by-step explanation:
The ionization equation is
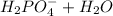 ⇄
⇄
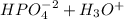 (1)
(1)
As the Bronsted definition sais, an acid is a substance with the ability to give protons thus, H2PO4 is the acid and HPO42- is the conjugate base.
The Ka expression is the ratio between the concentration of products and reactants of the equilibrium reaction so,
![Ka = ([HPO_(4)^(-2)] [H_(3)O^(+)])/([H_(2)PO_(4)^(-)] [H_(2)O]) = 6.2x10^(-8)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yjftcnyl4w6odmw0duiqfja4n74ljg4nvn.png)
The pKa is
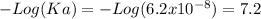
The pKa of H2CO3 is 6,35, thus this a stronger acid than H2PO4. The higher the pKa of an acid greater the capacity to donate protons.
In the body H2CO3 is a more optimal buffer for regulating pH due to the combination of the two acid-base equilibriums and the two pKa.
If the urine is acidified, according to Le Chatlier's Principle the equilibrium (1) moves to the left neutralizing the excess proton concentration.