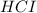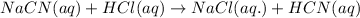Answer: a)
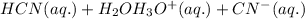
b)
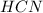 : acid
: acid
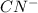 :conjugate base.
:conjugate base.
And,
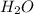 : base
: base
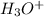 : conjugate acid.
: conjugate acid.
c)
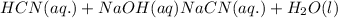
d)
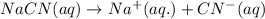
e)
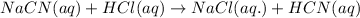
Step-by-step explanation:
a) Weak acid is defined as the acid which does not completely dissociates when dissolved in water. They have high pH. These releases
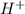 ions in their aqueous states.
ions in their aqueous states.
The equation for the dissociation of
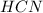 acid is given by:
acid is given by:
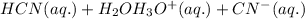
b) According to the Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory, an acid is defined as a substance which looses donates protons and thus forming conjugate base and a base is defined as a substance which accepts protons and thus forming conjugate acid.
For the given chemical equation:
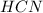 is loosing a proton, thus it is considered as an acid and after losing a proton, it forms
is loosing a proton, thus it is considered as an acid and after losing a proton, it forms
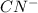 which is a conjugate base.
which is a conjugate base.
And,
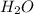 is gaining a proton, thus it is considered as a base and after gaining a proton, it forms
is gaining a proton, thus it is considered as a base and after gaining a proton, it forms
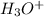 which is a conjugate acid.
which is a conjugate acid.
c) Neutralization reaction is a reaction in which an acid reacts with base to produce salt and water.
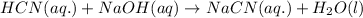
d) The chemical equation for dissociation of
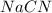 in water.
in water.
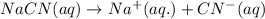
e) The chemical equation for the reaction of
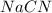 and
and