Answer:
domain [ g(t) ] = (-∞,∞)
g'(t)=9
domain [ g'(t) ] =(-∞,∞)
Explanation:
We start by finding the domain of the function g(t)
The domain of a function is the set of all inputs over which the function has defined outputs.
In g(t) = 9t ; g(t) is define for all real numbers
domain [ g(t) ] = (-∞,∞)
For the derivative of the function we use the definition of derivative :
Given f(x)→
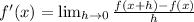
In our exercise :
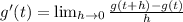
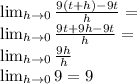
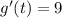
domain [ g'(t) ] =(-∞,∞)