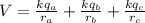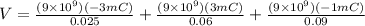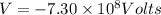Answer:
Part a)
tex]V = -1 \times 10^8 Volts[/tex]
Part b)
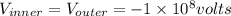
Part c)
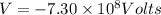
Step-by-step explanation:
Part a)
Net charge distribution on each shell is given as
On surface of radius "a"
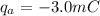
on radius "b"
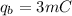
on radius "c"
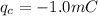
Now potential at the outer shell is
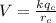
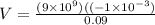
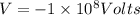
Part b)
Since copper sphere is a conducting sphere so here it will be an equi potential surface
So the potential will remain same throughout the surface of this sphere
Now we can say
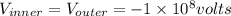
Part c)
Now electric potential at inner sphere is given as