Answer :
(a) The IUPAC name for
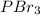 is phosphorous tribromide.
is phosphorous tribromide.
(b) The IUPAC name for
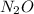 is dinitrogen oxide.
is dinitrogen oxide.
(c) The IUPAC name for
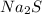 is sodium sulfide.
is sodium sulfide.
(d) The IUPAC name for
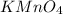 is potassium permanganate(VII).
is potassium permanganate(VII).
Explanation :
The nomenclature of covalent compound is given by:
1. The less electronegative element is written first.
2. The more electronegative element is written then, and a suffix is added with it. The suffix added is '-ide'.
3. If atoms of an element is greater than 1, then prefixes are added which are 'mono' for 1 atom, 'di' for 2 atoms, 'tri' for 3 atoms and so on..
The nomenclature of ionic compounds is given by:
1. Positive ion is written first.
2. The negative ion is written next and a suffix is added at the end of the negative ion. The suffix written is '-ide'.
3. In case of transition metals, the oxidation state are written in roman numerals in bracket in front of positive ions.
(a)
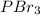 is a covalent compound because sharing of electrons takes place between phosphorous and bromine. Both the elements are non-metals and hence, will form covalent bond.
is a covalent compound because sharing of electrons takes place between phosphorous and bromine. Both the elements are non-metals and hence, will form covalent bond.
So, the IUPAC name for
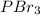 is phosphorous tribromide.
is phosphorous tribromide.
(b)
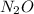 is a covalent compound because sharing of electrons takes place between nitrogen and oxygen. Both the elements are non-metals and hence, will form covalent bond.
is a covalent compound because sharing of electrons takes place between nitrogen and oxygen. Both the elements are non-metals and hence, will form covalent bond.
So, the IUPAC name for
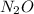 is dinitrogen oxide.
is dinitrogen oxide.
(c)
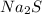 is an ionic compound because sodium element is a metal and sulfur element is a non-metal. The bond formed between a metal and a non-metal is always ionic in nature.
is an ionic compound because sodium element is a metal and sulfur element is a non-metal. The bond formed between a metal and a non-metal is always ionic in nature.
So, the IUPAC name for
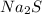 is sodium sulfide.
is sodium sulfide.
(d)
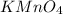 is an ionic compound. The bond formed between a metal and a non-metal is always ionic in nature.
is an ionic compound. The bond formed between a metal and a non-metal is always ionic in nature.
'Mn' is a transition metal and the oxidation state of 'Mn' is (+7)
The name of
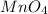 is permanganate.
is permanganate.
So, the IUPAC name for
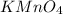 is potassium permanganate(VII).
is potassium permanganate(VII).