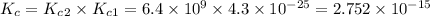Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The given equilibrium reaction is:
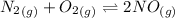
The expression for the equilibrium constant is:
![K_c_1=\frac {[NO]^2}{[N_2][O_2]}=4.3* 10^(-25)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/dnqtog67hyioqravfux6ierh2ppmdblhz4.png)
The another given equilibrium reaction is:
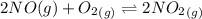
The expression for the equilibrium constant is:
![K_c_2=\frac {[NO_2]^2}{[NO]^2[O_2]}=6.4* 10^(9)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/svaxx6095wk32mi21njv3uvkfgv4sahvjb.png)
To find,
For the equilibrium which is:
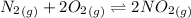
The expression for the equilibrium constant is:
![K_c=\frac {[NO_2]^2}{[N_2][O_2]^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/us1o2rw2l9gj2cjl9iackreafdbded9yd1.png)
Multiplying and dividing by
![[NO]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2wv6tqvxq4u1e9e7iz3w8xhqvx5p16rhsc.png) and rearranging in the above equation as:
and rearranging in the above equation as:
![K_c=\frac {[NO_2]^2}{[NO]^2[O_2]}* \frac {[NO]^2}{[N_2][O_2]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/12r1f7cmcm81k61nvtqlroa7qn5dah93ev.png)