Answer:
The absorbance of the myoglobin solution across a 1 cm path is 0.84.
Step-by-step explanation:
Beer-Lambert's law :
Formula used :
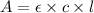
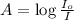
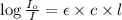
where,
A = absorbance of solution
c = concentration of solution
 = Molar absorption coefficient
= Molar absorption coefficient
l = path length
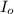 = incident light
= incident light
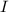 = transmitted light
= transmitted light
Given :
l = 1 cm, c = 1 mg/mL ,
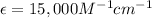
Molar mass of myoglobin = 17.8 kDa = 17.8 kg/mol=17800 g/mol
(1 Da = 1 g/mol)
c = 1 mg /mL =
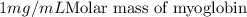
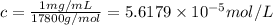
1 mg = 0.001 g, 1 mL = 0.001 L
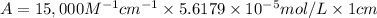
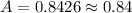
The absorbance of the myoglobin solution across a 1 cm path is 0.84.