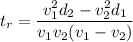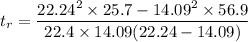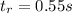Answer:
a)
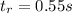
b) a = 5.59 m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
given,
total distance traveled by the car to stop is 56.9 m when speed of vehicle is 80 km/h or 80 × 0.278 = 22.24 m/s
total distance traveled by the car to stop is 25.7 m when speed of vehicle is 50.7 km/h or 50.7 × 0.278 = 14.09 m/s
using stopping distance formula
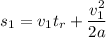 ................(1)
................(1)
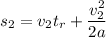 ..............(2)
..............(2)
on solving both the equation we get
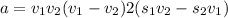
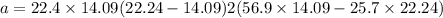
a = 5.59 m/s²
now reaction time calculation