Answer:
Attractive
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
Temperature = 426 K
Volume / moles = 1.31 L / mol
So, for n = 1 , V = 1.31 L
Using ideal gas equation as:
PV=nRT
where,
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
T is the temperature
R is Gas constant having value = 0.08314 L bar/ K mol
Applying the equation as:
P × 1.31 L = 1 × 0.08314 L bar/ K mol × 426 K
⇒P (ideal) = 27.0363 bar
Using Van der Waal's equation
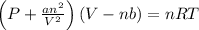
R = 0.08314 L bar/ K mol
Where, a and b are constants.
1 L = 1 dm³
For Ar, given that:
So, a = 1.355 bar dm⁶ / mol² = 1.355 bar L² / mol²
b = 0.0320 dm³ / mol = 0.0320 L / mol
So,
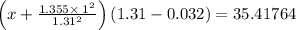
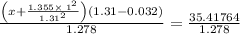
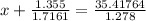
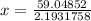
⇒P (real) = 26.9238 bar
Thus, P (real) is smaller than P (ideal) , the attractive force will dominate.