Answer:
The excess reactant is
 .
.
Left over = 1.9903 moles or 4.0122 g
Step-by-step explanation:
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
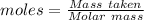
Given: For
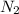
Given mass = 37.0 g
Molar mass of
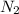 = 28.0134 g/mol
= 28.0134 g/mol
Moles of
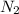 = 37.0 g / 28.0134 g/mol = 1.3208 moles
= 37.0 g / 28.0134 g/mol = 1.3208 moles
Given: For

Given mass = 12.0 g
Molar mass of
 = 2.0159 g/mol
= 2.0159 g/mol
Moles of
 = 12.0 g / 2.0159 g/mol = 5.9527 moles
= 12.0 g / 2.0159 g/mol = 5.9527 moles
According to the given reaction:
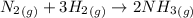
1 mole of
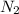 react with 3 moles of
react with 3 moles of

1.3208 moles of
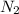 react with 3*1.3208 moles of
react with 3*1.3208 moles of

Moles of
 reacted = 3.9624 moles
reacted = 3.9624 moles
Available moles of
 = 5.9527 moles
= 5.9527 moles
Limiting reagent is the one which is present in small amount. Thus,
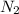 is limiting reagent as
is limiting reagent as
 is present in excess . (3.9624 < 5.9527)
is present in excess . (3.9624 < 5.9527)
The excess reactant is
 .
.
Left over = 5.9527 - 3.9624 moles = 1.9903 moles
Mass = moles × Molar mass = 1.9903 moles × 2.0159 g/mol = 4.0122 g
Left over is 4.0122 g of hydrogen.